Based On The Animation, Which Of The Following Is Cleaved By C1?
xi.3B: The Complement System
- Page ID
- 3271
Learning Objectives
- Briefly depict how the classical complement pathway is activated.
- Briefly describe the beneficial furnishings of the following complement pathway products:
- C5a
- C3a
- C3b
- C4b
- C3d
- C5b6789n (MAC)
- Briefly describe how the lectin pathway is activated.
- Briefly draw how the alternative complement pathway is activated.
In this section we will expect at how the body'southward complement system functions to remove infectious agents. The complement system refers to a serial of more xxx soluble, preformed proteins circulating in the blood and bathing the fluids surrounding tissues. The proteins circulate in an inactive grade, but in response to the recognition of molecular components of microorganism, they become sequentially activated, working in a pour where in the binding of ane protein promotes the binding of the next protein in the cascade. In that location are 3 complement pathways that brand up the complement system: the classical complement pathway, the lectin pathway, and the alternative complement pathway. The pathways differ in the manner in which they are initiated and ultimately produce a key enzyme called C3 convertase:
- The classical complement pathway is initiated past activation of C1. C1 is primarily activated by interacting with the Fc portion of the antibody molecules IgG or IgM after they have bound to their specific antigen. C1 is likewise able to directly demark to the surfaces of some pathogens equally well as with the C-reactive protein (CRP) that is produced during the acute phase response of innate immunity.
- The lectin pathway is activated by the interaction of microbial carbohydrates (lectins) with mannose-binding lectin (MBL) or ficolins found in the plasma and tissue fluids.
- The alternative complement pathway is activated by C3b binding to microbial surfaces and to antibody molecules.
The end results and defence force benefits of each pathway, nevertheless, are the aforementioned. All complement pathways bear out half dozen benign innate defense force functions. Proteins produced by the complement pathways:
- Trigger inflammation,
- Chemotactically attract phagocytes to the infection site,
- Promote the attachment of antigens to phagocytes (enhanced attachment or opsonization),
- Cause lysis of Gram-negative bacteria, homo cells displaying foreign epitopes,and viral envelopes,
- Play a function in the activation of naive B-lymphocytes during adaptive immunity, and
- Remove harmful allowed complexes from the body.
We will at present look at each of these complement pathways and come across how they function to protect the body.
The Classical Complement Pathway
The classical complement pathway is primarily activated when a complement poly peptide complex chosen C1 interacts with the Fc portion of the antibody molecules IgG or IgM subsequently they accept bound to their specific antigen via their Fab portion. C1 is also able to directly bind to the surfaces of some pathogens likewise as with the C-reactive poly peptide (CRP) that is produced during the acute phase response of innate immunity. The C1 circuitous is composed of 3 complement proteins called C1q, C1r, and C1s.
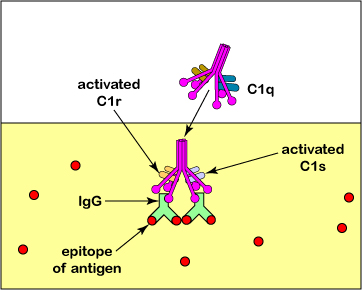
C1 is also able to directly bind to the surfaces of some pathogens as well as with the C-reactive protein (CRP) that is produced during the acute phase response of innate immunity.
Every bit mentioned higher up, proteins of the complement pathways carry out half dozen benign innate defense force functions. These include:
i. Triggering inflammation: C5a is the almost potent complement protein triggering inflammation. It reacts with blood vessels causing vasodilation. It also causes mast cells to release vasodilators such as histamine,increasing blood vessel permeability as well every bit increasing the expression of adhesion molecules on leukocytes and the vascular endothelium so that leukocytes can squeeze out of the claret vessels and enter the tissue (diapedesis). C5a also causes neutrophils to release toxic oxygen radicals for extracellular killing and induces fever. To a lesser extent C3a and C4a as well promote inflammation. As we will see later in this unit, inflammation is a process in which blood vessels dilate and become more permeable, thus enabling torso defence cells and defense chemicals to exit the claret and enter the tissues.
2. Chemotactically attracting phagocytes to the infection site: C5a also functions equally a chemoattractant for phagocytes. Phagocytes volition movement towards increasing concentrations of C5a and later on attach, via their CR1 receptors to the C3b molecules attached to the antigen. This will be discussed in greater detail afterward in this unit under phagocytosis.
3. Promoting the zipper of antigens to phagocytes (enhanced attachment or opsonization): C3b and to a bottom extent, C4b can function equally opsonins, that is, they can attach antigens to phagocytes. 1 portion of the C3b binds to proteins and polysaccharides on microbial surfaces; another portion attaches to CR1 receptors on phagocytes, B-lymphocytes, and dendritic cells for enhanced phagocytosis. (run into Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\)). In actuality, C3b molecule tin can bind to pretty much any poly peptide or polysaccharide. Human cells, however, produce Factor H that binds to C3b and allows Factor I to inactivate the C3b. On the other paw, substances such equally LPS on bacterial cells facilitate the binding of Factor B to C3b and this protects the C3b from inactivation by Factor I. In this mode, C3b does not collaborate with our own cells only is able to interact with microbial cells. C3a and C5a increment the expression of C3b receptors on phagocytes and increase their metabolic activity.
4. Causing lysis of Gram-negative bacteria, man cells displaying foreign epitopes,and viral envelopes: C5b6789 n , functions equally a Membrane Attack Circuitous (MAC). This helps to destroy gram-negative bacteria as well equally human cells displaying strange antigens (virus-infected cells, tumor cells, etc.) by causing their lysis; come across Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\) and Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\). It tin also harm the envelope of enveloped viruses.
five. Serving as a second betoken for activating naive B-lymphocytes during adaptive amnesty: Some C3b is converted to C3d. C3d binds to CR2 receptors on B-lymphocytes. This serves equally a second point for the activation of B-lymphocytes whose B-jail cell receptors accept only interacted with their corresponding antigen.
6. Removing harmful immune complexes from the body: C3b and to a lesser extent, C4b assistance to remove harmful immune complexes from the torso. The C3b and C4b attach the immune complexes to CR1 receptors on erythrocytes. The erythrocytes so deliver the complexes to fixed macrophages within the spleen and liver for devastation. Immune complexes tin lead to a harmful Type III hypersensitivity, as volition be discussed afterwards in Unit five under Hypersensitivities.
Exercise: Retrieve-Pair-Share Questions
- Some bacterial capsules are rich in sialic acid, a common component of host cell glycoprotein, that has an affinity for serum protein H, a complement regulatory protein that leads to the degradation of C3b.
Describe what significance this has in the bacterium resisting phagocytosis and why.
- Southward. pyogenes produces a protease that cleaves the complement protein C5a.
Describe what significance this has in the bacterium resisting phagocytosis and why.
The Lectin Pathway
The lectin pathway is activated by the interaction of microbial carbohydrates with mannose-binding lectin (MBL) or ficolins found in the plasma and tissue fluids. (Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins.) The lectin pathway is mediated by two groups of proteins found in the plasma of the claret and in tissue fluids:
1. Mannose-binding lectin (MBL) - as well known as mannose-binding poly peptide or MBP. MBL is a soluble pattern-recognition receptor that binds to various microbial carbohydrates such as those rich in mannose or fucose, and to North-acetylglucosamine (NAG). These glycans are common in microbial glycoproteins and glycolipids only rare in those of humans. MBL is synthesized by the liver and released into the bloodstream every bit role of the astute phase response that will be discussed later in this unit. The MBL is equivalent to C1q in the classical complement pathway.
Ficolins are like in their structure to MBL and bind to microbial carbohydrates such every bit N-acetylglucosamine (NAG), lipoteichoic acids, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Ficolin is also equivalent to C1q in the classical complement pathway.
ii. Both mannose-bounden lectin (MBL) and ficolin form complexes with MBL-associated serine proteases called MASP1 and MASP2, which are equivalent to C1r and C1s of the classical pathway.
The benign results of the activated complement proteins are the same every bit in the classical complement pathway higher up. The complement proteins:
i. Trigger inflammation : C5a>C3a>c4a;
ii. Chemotactically concenter phagocytes to the infection site: C5a;
iii. Promote the zipper of antigens to phagocytes via enhanced attachment or opsonization : C3b>C4b;
iv. Crusade lysis of Gram-negative bacteria and human cells displaying foreign epitopes : MAC;
v. Serve every bit a 2nd signal for the activation of naive B-lymphocytes ): C3d; and
6 Remove harmful immune complexes from the body: C3b>C4b.
The Alternative Complement Pathway
The alternative complement pathway is mediated past C3b, produced either by the classical or lectin pathways or from C3 hydrolysis by water. (H2o can hydrolyze C3 and form C3i, a molecule that functions in a manner similar to C3b.)
Activation of the alternative complement pathway begins when C3b (or C3i) binds to the cell wall and other surface components of microbes. C3b tin also bind to IgG antibodies. Alternative pathway poly peptide Cistron B and so combines with the cell-bound C3b to class C3bB. Gene D then splits the bound Cistron B into Bb and Ba, forming C3bBb. A serum protein called properdin and so binds to the Bb to form C3bBbP that functions as a C3 convertase (see Figure \(\PageIndex{xiii}\)) capable of enzymatically splitting hundreds of molecules of C3 into C3a and C3b. The alternative complement pathway is at present activated.
Some of the C3b subsequently binds to some of the C3bBb to form C3bBb3b, a C5 convertase capable of splitting molecules of C5 into C5a and C5b (see Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\)). From here, the culling complement pathway is identical to the other complement pathways.
The benign results are the same as in the classical complement pathway higher up. The complement proteins:
- Trigger inflammation : C5a>C3a>c4a;
- Chemotactically attract phagocytes to the infection site: C5a;
- Promote the zipper of antigens to phagocytes via enhanced attachment or opsonization : C3b>C4b;
- Cause lysis of Gram-negative bacteria, human cells displaying foreign epitopes,and viral envelopes: MAC; and
- Serve equally a second signal for the activation of naive B-lymphocytes ): C3d;
- Remove harmful immune complexes from the trunk: C3b>C4b.
Go along in mind that in Unit 3, nosotros learned several mechanisms that diverse leaner apply to resist the body's complement pathways. Past resisting these firsthand innate allowed defenses, some bacteria accept a better take chances of colonizing their host.
Summary
- The proteins of the complement organisation broadcast in an inactive class, but in response to the recognition of molecular components of microorganism, they become sequentially activated, working in a cascade where in the binding of one poly peptide promotes the binding of the next poly peptide in the cascade.
- There are 3 complement pathways that brand upwards the complement system: the classical complement pathway, the lectin pathway, and the alternative complement pathway.
- The classical complement pathway is initiated past activation of C1. C1 is primarily activated past interacting with the Fc portion of the antibody molecules IgG or IgM after they accept bound to their specific antigen. C1 is also able to directly demark to the surfaces of some pathogens as well as with the C-reactive poly peptide (CRP) that is produced during the acute phase response of innate amnesty.
- The lectin pathway is activated by the interaction of microbial carbohydrates (lectins) with mannose-binding lectin (MBL) or ficolins found in the plasma and tissue fluids.
- The alternative complement pathway is activated by C3b binding to microbial surfaces and to antibody molecules.
- All complement pathways carry out the aforementioned 6 beneficial innate defense functions.
- The complement proteins C5a and, to a lesser extent, C3a, and C4a trigger vasodilation and inflammation in order to deliver defense cells and defence force chemicals to the infection site.
- The complement protein C5a also functions every bit a chemoattractant for phagocytes.
- The complement proteins C3b and to a bottom extent, C4b tin can function as opsonins, that is, they can attach antigens to phagocytes.
- The complement proteins C5b6789n, functions as a Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) causing lysis of Gram-negative bacteria, human cells displaying foreign epitopes, and viral envelopes.
- The complement protein C3d serves as a 2d signal for activating naive B-lymphocytes during adaptive amnesty.
- The complement proteins C3b and to a bottom extent, C4b help to remove harmful immune complexes from the body.
Source: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Microbiology/Book:_Microbiology_%28Kaiser%29/Unit_5:_Innate_Immunity/11.3:_Immediate_Innate_Immunity/11.3B:_The_Complement_System
Posted by: brumfieldgince1938.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Based On The Animation, Which Of The Following Is Cleaved By C1?"
Post a Comment